Fermi Hole and Coulomb Hole
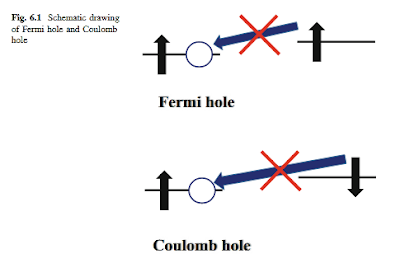
Electron belongs to Fermi particle. In quantum mechanics, more than two Fermi particles are not allowed to have the same quantum state. Figure 6.1 depicts the schematic drawing of Fermi hole and Coulomb hole. When one a electron exists in the specific spatial orbital, another a electron is not allowed to be allocated in the same spatial orbital. The hole of the spatial orbital is called Fermi hole. On the other hand, two electrons with different spins are allowed to be allocated in the same spatial orbital. However, when Coulomb repulsion between two electrons is much larger, two electrons are not allowed to be allocated in the same spatial orbital. The hole is called Coulomb hole. In Hartree-Fock method, though Fermi hole is reproduced, Coulomb hole cannot be quantitatively reproduced. It is because the strength of Coulomb repulsion between two electrons is treated in an average manner.
Quantum computational chemistry : modelling and calculation for functional materials


No comments:
Post a Comment